Order Book Trading Analysis
Order Book Trading Analysis
An order book can be used for quantifying the market’s intentions in the short term.
“With the advent of electronic trading, markets have moved to a system in which liquidity provision has become decentralized...The rule-driven execution of orders in these limit order books and the extensive data that is available for order-driven markets makes them ideal candidates for stochastic modeling.” (2)
What is an Order Book?
An order book is a ledger showing the Depth of the Market (DoM) consisting of a complete list of buying and selling orders for a particular financial-traded asset at a particular time. Every trading order in the book includes price and volume. Every exchange uses an order book to record, match, and execute trading orders.
Order Book -The Basics
(1) The book includes all buy and sell orders, plus the order history
(2) Order books improve market transparency as they can show market depth to every participant
(3 The order book is updated in real time throughout the trading day
(4) The highest bid (buy) and the lowest ask (sell) are called the top of the book. The difference between these top bid/ask prices is the spread
(5) Every order that is not yet executed, can be canceled
(6) The book can be visualized via the market depth chart that contains all active bids/asks
(7) The order book includes all the ‘Makers’ and none of the ‘Takers’
Makers and Takers
□ Traders who place a Buy/Sell order that is instantly matched and filled are called Takers. These orders do not go on the order book.
□ Traders who place a Buy/Sell order that cannot be matched and filled instantly at the current market are called Makers. These orders are included in the order book.
Why an Order Book is useful to Analysts?
An order book is useful for the short-term analysis of any market. This is how:
(1) It can be used for the discovery of the general market sentiment by measuring the market depth
(2) It can highlight order imbalances that may affect the short-term dynamics of demand/supply
(3) It can pinpoint upcoming support and resistance price levels
(4) It can confirm the growth of volume activity. Statistically, there is a strong linear relationship between the growth of the order book and the growth of volume activity
(5) It can uncover market manipulation (check below)
Price Levels & Book Depth
In the case of several orders targeting a common price, they are called a price level. The number of price levels available is called the Book Depth.
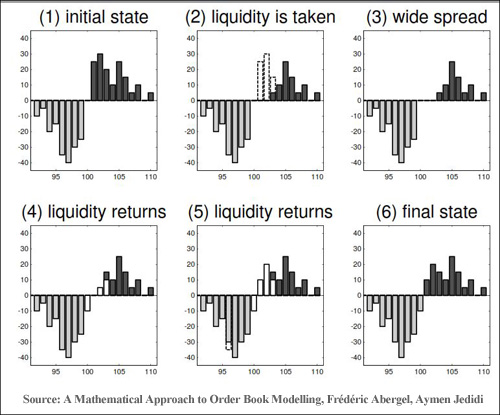
Crossed book
An order book is said to be crossed where the bid (buy) price is equal to or above the lowest ask (sell) price. This may be happening due to technical inefficiencies.
Order Book Manipulation
Any trader can place a limit order in the book and cancel it later before this order is executed. If we are talking about a small retail order this action does not affect the market. In antithesis, if the order that is placed and canceled is huge, then this action can have a great impact on the market and can be seen as a sign of manipulation. The unstable nature of an order book creates considerable obstacles to the analysis of the book.
Understanding Price Walls
Price Walls can be either Bid or Ask Walls. A bid wall occurs when a huge single order or a composition of too many smaller orders is placed at the same price level in the order book.
A price wall can be the outcome:
(i) A considerably wealthy individual enters the market and wants to attract the big ‘fishes’ so his orders get filled fast
(ii) A market maker tries to stabilize choppy market conditions by placing a price wall against the short-term trend
(iii) Someone tries to manipulate the general market sentiment by placing a huge limit order to control the distribution of new orders above/below the wall. Retail traders are highly affected by these price walls and modify their orders to move above/below this wall. Afterward, the price wall is removed and what is left in the market is the newer orders by retail traders. The manipulator now places orders in the opposite direction and buys all the positions of retail traders.
Measuring the Market Depth by Using the Order Book
Market Depth
There are many ways to measure the market depth via the use of the order book:
(1) By summarizing the number of all the buy orders and sell orders available in the book (measures retail trader’s actions)
(2) By summarizing all the bids and asks multiplied by their respective price (measures total market actions)
(3) By summarizing all the bids and asks multiplied by their respective price, but by filtering all orders via a Decay Formula. In simple words, the quantity decreases at a rate proportional to the current price. The Decay Formula will provide extra weight to bids/asks placed close to the current price and reduce weight to bids/asks placed far away from the current price. This is useful to minimize the effect of fake orders that tend to get canceled before being filled.
□ The closer to the current market price → the more weight
□ The further from the current market price → the less weight
Something very important for Forex traders is that the Depth of Market (DoM) of Over-The-Counter (OTC) financial instruments can be modified by the quotes of the broker. Brokers may provide different prices depending on bid/ask volume.
Other Statistics
There are quite a few other useful statistics generated from the Order Book. These are some examples:
-
Average Size of Limit Orders
-
Average Time Between Limit Orders
-
Number of Cancellation Orders
-
Average Size of Cancellation Orders
-
Average Time Between Cancellation Orders
References:
(1) (Image) A Mathematical Approach to Order Book Modelling, Frédéric Abergel, Aymen Jedidi
(2) (Quote) Reconstructing the Order Book, Kunal Khanna, Michael Smit, David Wu, and Tony Zhang
■ Forex Order Books
George Protonotarios, for CurrenciesFx.com
November, 5th, 2019
> READ MORE ON RESEARCH