Researching the Foreign Exchange Market based on facts, historical data, and the cyclical patterns of the past.
Forex Market Statistics
With a daily turnover of $7.5 trillion per day, the Foreign Exchange Market is the largest and most liquid financial market worldwide.
Highlights
- The size of the entire Foreign Exchange market is estimated to be over 2.4 quadrillion USD
- More than 170 currencies are traded on the global Foreign Exchange market
- USD is a component of 88.5% of the overall FX trading turnover, while EUR/USD remains the largest currency pair (22.7%)
- London remains the most important Forex center in the world, followed by New York
- Five organizations hold a 44% share of the entire global Forex market
- There are over 14 million active Forex traders worldwide, most of them are located in Asia, and the great majority of them are men (89%)
- Retail trading accounts account only for 5.5% of the entire market’s turnover
- The MetaTrader platforms dominate the online Foreign Exchange market (91%)
» More on Forex Market Statistics
Forex Market Volumes
Volume is a leading market indicator that can help traders recognize strong trends and reversals, but also identify the current market phase and think ahead of the current price action.
-
The US dollar remains the dominant vehicle currency, being on one side of 88% of all Forex transactions (Euro 31%)
-
The Foreign Exchange market's daily volumes average over 5.0 trillion USD
-
FX swaps transactions reach 2.4 trillion USD per day (Forex traders are showing an increasing interest in derivatives contracts)
-
Options and Similar products reach 0.25 trillion USD per day
-
Five countries (UK, USA, Singapore, Hong Kong, and Japan) contribute 77% of all Foreign Exchange transactions
» More on Forex Market Volumes
Investigating the Cyclical Patterns of Exchange Rates
Based on research starting in January 2000 and ending in October 2018, these are the average monthly returns of the 7 major currency pairs.
Table: Comparing the performance of 7 Forex pairs (Source: G. Protonotarios for CurrenciesFx.com)
| PERFORMANCE | EURUSD | GBPUSD | USDJPY | USDCAD | USDCHF | AUDUSD | NZDUSD |
| MONTH | (PER MONTH) | ||||||
| (1) JANUARY | -0.66% | 0.08% | -0.13% | 0.50% | 0.34% | -0.14% | -0.36% |
| (2) FEBRUARY | -0.36% | -1.02% | 0.25% | 0.19% | 0.05% | 0.22% | -0.03% |
| (3) MARCH | 0.32% | -0.10% | 0.51% | -0.22% | -0.26% | 0.32% | 0.26% |
| (4) APRIL | 0.78% | 1.30% | 0.05% | -1.11% | -0.34% | 1.29% | 0.90% |
| (5) MAY | -0.72% | -0.57% | -0.09% | -0.18% | 0.45% | -1.12% | -0.80% |
| (6) JUNE | 0.62% | 0.42% | -0.22% | -0.17% | -0.92% | 0.85% | 0.67% |
| (7) JULY | 0.11% | 0.24% | -0.22% | 0.04% | -0.03% | 0.20% | 0.14% |
| (8) AUGUST | -0.19% | -0.94% | -1.13% | 0.08% | 0.04% | -1.07% | -0.94% |
| (9) SEPTEMBER | 0.40% | 0.39% | 0.25% | -0.31% | 0.06% | -0.13% | 0.11% |
| (10) OCTOBER | -0.70% | -0.37% | -0.20% | 0.73% | 0.15% | 0.32% | 0.46% |
| (11) NOVEMBER | 0.12% | -0.24% | 0.89% | -0.03% | -0.26% | -0.14% | 0.15% |
| (12) DECEMBER | 1.40% | 0.05% | 0.91% | 0.18% | -1.64% | 0.55% | 1.76% |
» Find the books of Giorgos Protonotarios (Amazon) | » More on the Forex Trading Calendar
Following the Smart Money
Smart money can be defined as the capital invested by traders with expert knowledge and often with inside information. Smart money can spot trends before others and trades basically against the general market sentiment.
Our research includes the following indicators:
-
Following the Long-Term Circles of Unemployment, Inflation, and Growth
-
COT Analysis (Commitment of traders)
-
The US-Dollar Index (USDX)
-
The CBOE Volatility Indexes (VIX & Skew Index)
-
The Treasury Bills Correlations
Intermarket Analysis
Intermarket Analysis investigates the relationships between different financial markets. The following intermarket analysis focuses on four major asset classes: bonds, currencies, equities, and commodities.
-
The Complicated Role of the US Dollar
-
US Dollar and Gold Price Adverse Relation
-
Crude Oil Relationships
-
EUR/USD & USDJPY Correlation to Equity Prices
-
Treasury Bills Correlation to the Forex and Equity Markets
-
Industrial Metals Correlation to Equity Prices
» More on Intermarket Analysis
Cross-Asset Correlations
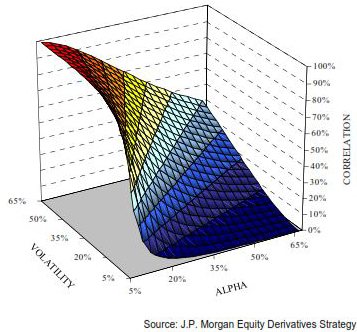 During periods of macro uncertainty, investors tend to see equities, soft commodities, energies, and corporate bonds as sources of unwanted portfolio risk. This phenomenon creates an increased relationship between macro uncertainty, volatility, and cross-market correlations. A cross-asset correlation measures the degree to which the price of a financial instrument is affected by a change in the price of another instrument of a different asset class. In general, a correlation between two variables expresses an average relationship that is backed by historical data. The correlation coefficient receives values between -1.0 and +1.0, and that means:
During periods of macro uncertainty, investors tend to see equities, soft commodities, energies, and corporate bonds as sources of unwanted portfolio risk. This phenomenon creates an increased relationship between macro uncertainty, volatility, and cross-market correlations. A cross-asset correlation measures the degree to which the price of a financial instrument is affected by a change in the price of another instrument of a different asset class. In general, a correlation between two variables expresses an average relationship that is backed by historical data. The correlation coefficient receives values between -1.0 and +1.0, and that means:
-
+1.0 is the perfect correlation reflecting identical movements/directions
-
-1.0 is the perfect negative coefficient reflecting identical opposite directions
» More on Cross-Asset Correlations
Forex Institutional Trading
Institutional traders are large players managing great sums of trading capital. They include Investment Banks, Hedge Funds, Mutual Funds, Investment Firms, and some large Commercial Corporations. Institutional traders can manage their funds but also their clients’ funds. The Euromoney Survey can provide a good insight into the top institutional players in the Forex market.
Table: Comparing Institutional Traders to Retail Traders
|
|
Institutional Trader |
Retail Trader |
|---|---|---|
|
Available Capital |
Holding 2 Million USD to many Billions USD |
Holding on average 6,600 USD (US average deposit) |
|
Positioning in the Market |
|
|
|
Horizon |
Long-Term |
Short-Term |
|
Trading Chart |
No Specific Timeframe |
M5 to D1 |
|
Financial Instruments |
|
|
|
Main Analysis Framework |
|
|
|
Typical Leverage |
1:1 to 20:1 |
10:1 to 200:1 |
|
Risk Management |
|
|
» More on Forex Institutional Traders and Order Flows
Trading the Order Book
An order book is a ledger showing the Depth of the Market (DoM) consisting of a complete list of buying and selling orders for a particular financial-traded asset at a particular time. Every trading order in the book includes price and volume. Every exchange uses an order book to record, match, and execute trading orders.
-
The book includes all buy and sell orders, plus the order history, and improves market transparency
-
The order book is updated in real-time throughout the trading day
-
The highest bid (buy) and the lowest ask (sell) are called the top of the book
-
The book can be visualized via the market depth chart that contains all active bids/asks
-
The order book includes all the ‘Makers’ and none of the ‘Takers’
■ Getting Started with Trading Research
CurrenciesFx.com (c)
