The Foreign Exchange market is a global decentralized (OTC) market for the trading of the world's currencies. Currency is a medium of exchange issued by a government body and is used as a method of payment.
Starting a Currency Trading Account (FAQ)
To trade the Forex market you need a trading account. There are several different types of accounts, however, it is highly recommended to start by opening a free demo account. A demo account can help you gain experience without any risk of losing your funds. Every respectful Forex broker will provide you with a free demo account. After gaining some experience, you can trade for real money. When starting to trade for real money note that a micro-lot account is more suitable for beginners.
- Demo/Practice accounts offer an excellent chance to gain experience and evaluate the conditions of every Forex Broker without any cost
- A micro-lot account is the best option for beginners and semi-advanced Forex Traders as it allows trading in smaller order sizes
» Opening a Forex Trading Account (FAQ)
Currency Market Trading Sessions
The Forex Market is open 24 hours a day from Monday to Friday. The best days to trade Forex are Tuesday, Wednesday, and Thursday. Overlaps offer high liquidity and wider volatility. The overlap between London and New York sessions offers the best opportunities for Forex trading from 12:00 to 14:00 GMT
GMT Market Overlaps
- London (European) session: 08:00 am to 16:00
- New York (American) session: 13:00 to 22:00
- Asian session: 22:00 to 09:00
» More on Forex Market Hours and Trading Sessions
The 4 Forex Lessons
CurrenciesFx provides extensive educational resources for all currency traders and investors. In the 4 following trading lessons, there are tips and advice from professional Forex traders:
(1) Market Sentiment: Market sentiment refers to the prevailing attitude of investors in a particular market.
These are some key takeaways
- Always consider whether your idea is already discounted by the market
- Make sure there are a lot of people who are going to be wrong if your idea is correct
- Think contrarian to the herd, the herd is destined to lose money
- A technical pattern is more likely to be confirmed when it is less observed and less discussed
- Don't Focus on what the market's going to do, focus on your action if it gets there
(2) Market Analysis: Market analysis refers to the process of studying market fundamental data and measuring the dynamics of future demand and supply to identify risks and spot trading opportunities.
These are some key takeaways
- Create the macroeconomic picture of tomorrow in your mind
- Imagine different configurations of the financial world and then create alternative scenarios, don't try to predict with certainty
- Markets are never wrong, however, opinions can often be wrong, so be ready to change your opinions
- Listen to what large investors and other big players are saying, but don't trust bankers
(3) Money Management: Money management refers to a set of rules that aims to minimize your losses in the short term and maximize your profits in the long term.
These are some key takeaways:
- To fail is to learn and a losing trade doesn’t necessarily mean a bad trade
- Never overtrade, prefer to trade small positions by protecting your trading capital
- Accept only trades with a Reward/Risk ratio of more than 3
- Hold your winners and run your profits
(4) Forex Trading Rules: Trading is a zero-sum game, and as a few people are making a lot of money, there must be a lot of others who lose. That means that basically, you should trade against the crowd.
These are some key takeaways:
- Be willing to take what the market has to offer
- Don’t try to buy the Bottom, try to buy the easy part of the trade
- The wise trader, every day assumes that all his positions are wrong
World's Currencies History
 Gold has been the global currency since the dawn of time. The Athenian silver drachma, coined in the 5th century B.C. is probably the first currency that became widely accepted, outside its issuing state. After Alexander the Great's conquests (336 BC – 323 BC), the name drachma was used in many of the Hellenistic kingdoms in the Middle East. The Greek Drachma was followed by the Roman Gold Aureus and Silver Denarius. The Athenian Drachma and the Roman Denarius circulated simultaneously for some time. The dominance of Roman currency was brought to an end because of the extreme inflation during the early 4th century A.D.. As the Western Roman Empire was falling, the Byzantine currency (named Gold Solidus) became the dominant currency worldwide in the 6th century A.D., and afterward. The Islamic Dinar became the next global currency during the next couple of centuries, although the Solidus and Islamic Dinar continued to circulate simultaneously for some time.
Gold has been the global currency since the dawn of time. The Athenian silver drachma, coined in the 5th century B.C. is probably the first currency that became widely accepted, outside its issuing state. After Alexander the Great's conquests (336 BC – 323 BC), the name drachma was used in many of the Hellenistic kingdoms in the Middle East. The Greek Drachma was followed by the Roman Gold Aureus and Silver Denarius. The Athenian Drachma and the Roman Denarius circulated simultaneously for some time. The dominance of Roman currency was brought to an end because of the extreme inflation during the early 4th century A.D.. As the Western Roman Empire was falling, the Byzantine currency (named Gold Solidus) became the dominant currency worldwide in the 6th century A.D., and afterward. The Islamic Dinar became the next global currency during the next couple of centuries, although the Solidus and Islamic Dinar continued to circulate simultaneously for some time.
By the 13th century, Florence Fiorino became dominant in the Mediterranean, and by the 15th century the Venice Ducato. In the 17th and early 18th centuries, the dominant international currency was the Dutch Guilder issued by the Netherlands. In the 19th century and until World War 2 the British Pound Sterling became the world’s dominant currency. In early 1900, 60% of the total global trade was invoiced in British Sterling. After WW2, and ever since the US Dollar has been the global dominant monetary unit.
Monetary Empires and Historical Patterns
The legendary hedge fund manager Ray Dalio offers an insight into the dynamics that he saw when studying the rises and declines of the last three reserve currency empires (the Dutch, the British, and the American) and the six other significant empires (Germany, France, Russia, India, Japan, and China) over the last 500 years. Always according to Ray Dalio, the following 17 items are the main forces that drive the rises and declines of monetary empires:
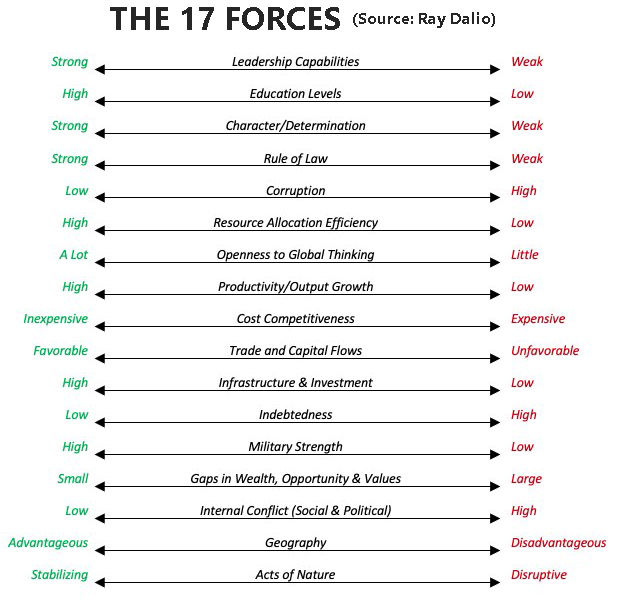
» More on World's Currencies History
Central Banks
A central bank is an institution providing financial stability for the economy. Central banks are responsible for implementing their country's monetary policy by adjusting the level of interest rates.
- Central banks adjust the level of interest rates to achieve price stability and high employment in the economy
- Most major central banks target a 2-3% annual inflation rate
» Central Banks Around the World
Credit Ratings and Agencies
Credit ratings provide global investors with insight into the level of risk associated with a particular country. Credit rating agencies offer information about whether bond issuers can meet their future obligations. There are three major rating agencies: Standard & Poor's, Moody's, and Fitch
» More on Credit Ratings and Agencies
Starting to Trade the Major Exchange Rates
An exchange rate refers to the rate at which one currency will be exchanged for another currency. The most actively traded pairs on the currency market are EUR/USD, GBP/USD, USD/JPY, and USD/CHF. These 4 pairs along with the 3 so-called commodity currency pairs: USD/CAD, AUD/USD, and NZD/USD are called the Forex Majors.
The Forex Majors refer to the most active and liquid currency pairs and account for about 85% of the total Foreign Exchange market activity. Based on G. Protonotarios' research (January 2000 to October 2018) this is the periodic performance of 7 major Forex pairs.
EURUSD
The Euro against the US Dollar is the most active and liquid pair in the whole Forex Market. Based on historical statistics, the best months to go long are December and June, and the best months to go short are May and October.
-
EURUSD accounts for 28.5% of the total Foreign Exchange market volume
-
US Dollar Index → 57.6% EUR weight
» The Euro against the US Dollar (EURUSD)
GBPUSD
The British Sterling against the US Dollar (GBPUSD) is a very liquid Forex pair. Based on historical statistics, the best months to go long are April and June, and the best month to go short is May.
-
GBPUSD accounts for about 11.4% of the Foreign Exchange market volume
-
US Dollar Index → 11.9% British Pound weight
» The British Pound Sterling against the US Dollar (GBPUSD)
USDJPY
The US Dollar against the Japanese Yen is a volatile and liquid Forex pair when measured on a daily and intraday basis
-
USDJPY accounts for 21.8% of the total Foreign Exchange market volume
-
US Dollar Index → 13.6% Japanese Yen weight
» The US Dollar against the Japanese Yen (USDJPY)
USDCAD
The US Dollar against the Canadian Dollar. USDCAD is a medium-volatility financial asset and a relatively liquid Forex pair.
-
USDCAD is highly correlated to the price of crude oil.
-
US Dollar Index → 9.1% Canadian Dollar weight
» The US Dollar against the Canadian Dollar (USDCAD)
USDCHF
The US Dollar against the Swiss Franc (USDCHF). The Swiss Franc and the US Dollar are both significant reserve currencies.
-
USDCHF accounts for 4.4% of the total Foreign Exchange market volume.
-
US Dollar Index → 3.6% Swiss Franc weight
» The US Dollar against the Swiss Franc (USDCHF)
AUDUSD
The Australian Dollar against the US Dollar. AUDUSD is a highly volatile Forex pair when measured on a daily and intraday basis.
-
During the past two decades, AUDUSD has had an 80% positive correlation to the price of gold and a 90% positive correlation to the New Zealand dollar.
-
The correlation between copper and Aussie is more than 70%.
-
AUDUSD accounts for 6.5% of the total Foreign Exchange market volume.
» The Australian Dollar against the US Dollar (AUDUSD)
NZDUSD
The New Zeeland Dollar against the US Dollar. NZDUSD is a highly volatile Forex pair on a day-to-day basis.
-
New Zealand is a major exporter of raw materials, and NZD is a commodity currency.
» The New Zeeland Dollar against the US Dollar (NZDUSD)
■ Getting Started with CurrenciesFx.com
CurrenciesFx.com (c)
