 Sovereign Credit Rating
Sovereign Credit Rating
Credit ratings provide insight regarding the level of risk associated with a particular country.
-
Credit rating agencies offer information about whether bond issuers can meet their future obligations
-
There are three major rating agencies: Standard & Poor's, Moody's, and Fitch
Investment Grades per Agency
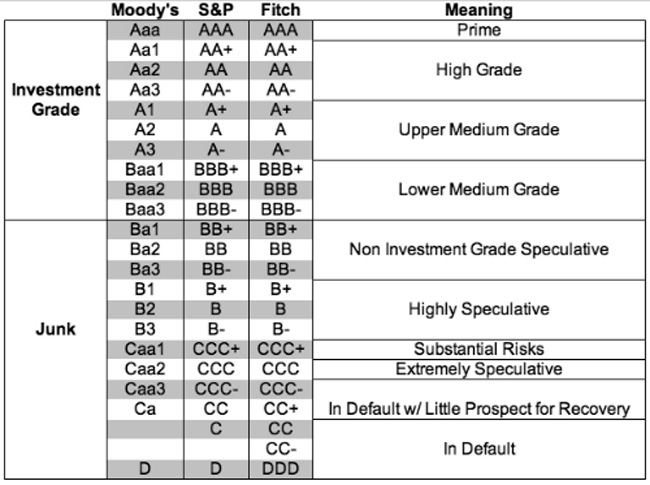
□ Moody’s considers a Baa3 or higher rating to be of investment grade, Ba1 and below is considered speculative
□ Standard & Poor's considers BBB- or higher rating to be investment grade, and BB+ or lower is considered to be speculative or "junk" grade
□ Fitch, like S&P, considers BBB- or higher rating to be investment grade, and BB+ or lower is considered to be speculative or "junk" grade
The Short History of Credit Ratings
The country's credit ratings were introduced at the beginning of the twentieth century. Moody's and other agencies were taken by surprise after the effects of the Great Depression when 21 out of 58 nations defaulted between 1930 and 1935.
Credit Ratings -The three (3) Agencies
Obtaining a favorable sovereign credit rating means a country pays a lower interest rate. There are three major credit agencies worldwide: S&P, Moody’s, and Fitch.
-
S&P was founded in 1917 and operates in New York
-
S&P Global recently reported revenue of 8.3 billion USD
-
The group has over 35,000 employees
-
Moody's is issuing credit ratings for debt securities
-
Moody's was founded in 1909 and it is headquartered in New York
-
The Moody's Investors Service has over 5,000 employees
-
The Moody's group has over 13,000 employees in more than 40 countries
-
Moody's Corporation recently reported revenue of $6.2 billion (Moody's Investors Service 400+ million USD)
-
Fitch was founded in 1913 and operates in New York and London, UK
-
4,000 employees, including more than 1,600 analysts
-
Recently reported revenue of 1.7 billion USD
Basic Ratings of all Agencies
In the following table, the basic credit rating categories and their meaning (three agencies):
Key Factors Affecting Credit Ratings
A country's credit rating includes a wide variety of variables:
(i) Current macroeconomic conditions
-
Growth, government deficits, government debt, etc.
(ii) Business conditions
-
General business conditions in the economy, including corporate legislation.
(iii) Changing macro environment
-
Opportunities and threats in the Macro environment
(iv) Political risk
-
Political stability plays a major role.
(v) Social conditions
-
Social unrest can lead to political instability.
(vi) History of defaulting
-
Countries with a record of defaulting get lower credit scores.
(vii) Geo-strategic factors
-
The likelihood of war or other major geopolitical events leads to increased military spending and higher government deficits.
■ Credit Ratings and Agencies
CurrenciesFx.com (c)
> READ MORE

